Nyheder om genbrug
Lås op for effektivitet: Din ultimative guide til at vælge den korrekte størrelse på den plastgranulatorsigte
For indkøbere af industrielt udstyr, ingeniører og teknisk personale inden for plastforarbejdning og genbrug er granulatoren en kernekraft. Men dens effektivitet og kvaliteten af dens output – den genopformulerede proces – afhænger i afgørende grad af én ofte overset komponent: sigten. At vælge den korrekte størrelse på granulatorsigten er ikke bare en mindre detalje; det er en beslutning, der påvirker gennemløbshastighed, partikelkonsistens, energiforbrug og endda levetiden for dit udstyr.
Denne guide vil gennemgå alt, hvad du behøver at vide for at træffe en informeret beslutning, og sikre, at du vælger den optimale skærmstørrelse til din specifikke applikation. Lad os dykke ned i det!
Hvad er en granulatorsigte, og hvorfor er den så vigtig?
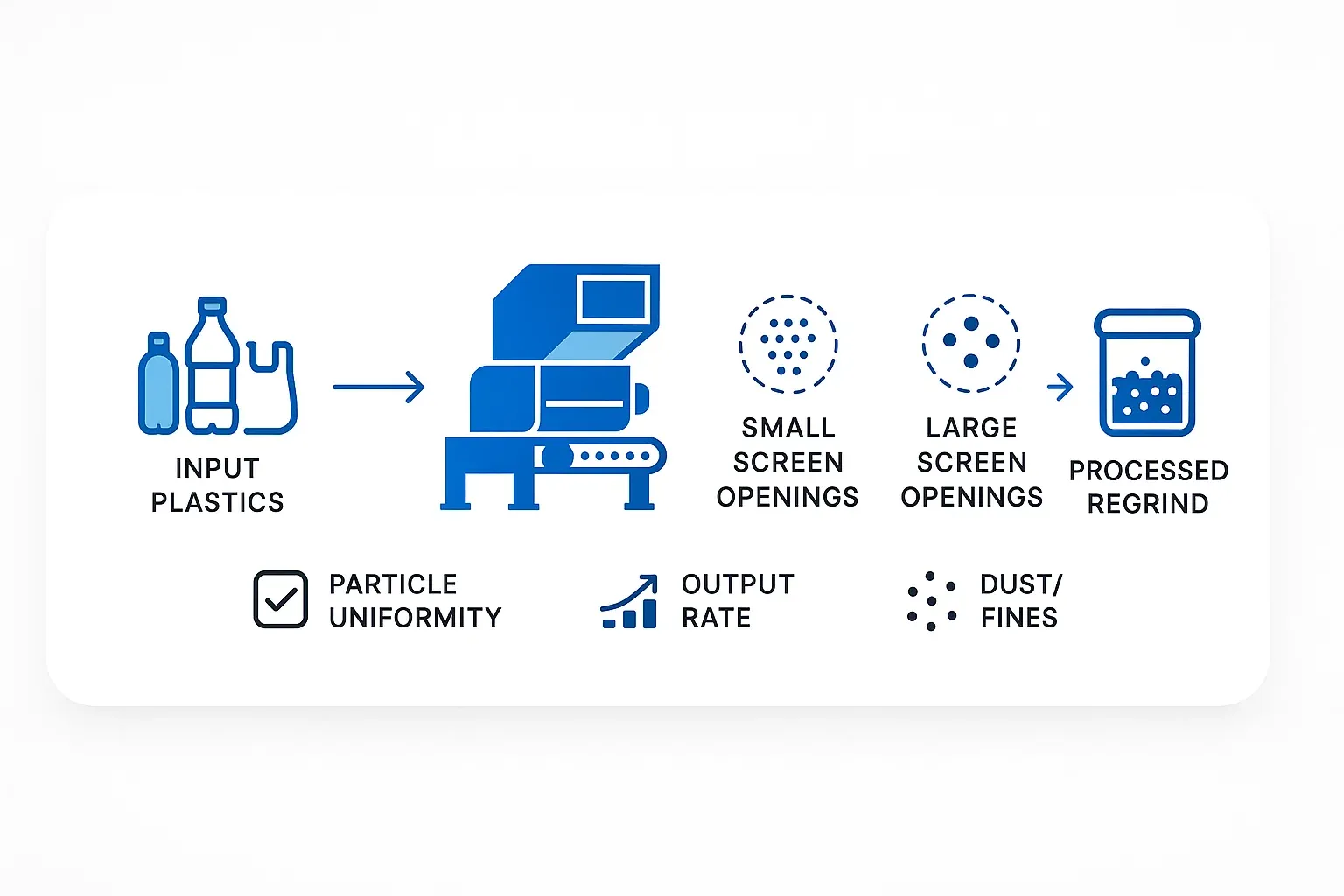
I sin kerne, en plast granulator reducerer størrelsen af plastaffald, udløbere, udrensninger eller kasserede dele til mindre, ensartede partikler kaldet "genformaling". Granulatorsigten, typisk en perforeret metalplade, er placeret under skærekammeret. Når rotorknivene skærer plasten, presses materialet gennem sigtens huller.
Skærmens primære funktioner er:
- At kontrollere maksimal partikelstørrelse af genformalingen. Materialet forbliver i skærekammeret, indtil det er lille nok til at passere gennem sigteåbningerne.
- At bidrage til ensartethed af genformalingen.
Hvorfor er dette afgørende?
- Genslibningskvalitet: Størrelsen og konsistensen af din genformaling påvirker direkte dens genbrugelighed i efterfølgende processer (f.eks. sprøjtestøbning, ekstrudering). Inkonsistente eller overdimensionerede partikler kan forårsage forarbejdningsproblemer, mens for store fine partikler kan føre til materialehåndteringsproblemer og smelteuoverensstemmelser.
- Gennemstrømning og effektivitet: Sigtestørrelsen påvirker, hvor hurtigt materialet forlader skærekammeret. En forkert dimensioneret sigte kan skabe flaskehalse, reducere gennemløbshastigheden og øge energiforbruget.
- Udstyrsslid: En dårligt tilpasset sold kan føre til øget slid på knivene og selve solden samt belaste granulatorens motor og drivkomponenter unødigt.
Nøglefaktorer, der påvirker valget af din granulatorsigtestørrelse
At vælge den rigtige skærmstørrelse er en balancegang. Her er de primære faktorer at overveje:
Ønsket slutpartikelstørrelse (specifikation for omslibning):
Dette er ofte udgangspunktet. Hvilken størrelse genformaling kræver din downstream-proces? Hvis du genintroducerer genformaling i jomfrueligt materiale til støbning, skal det typisk have en størrelse og form, der ligner de jomfruelige pellets, for at opnå ensartet smelte og flydeevne.
Generel regel: Sigtehullets diameter er generelt lidt større end den ønskede maksimale partikelstørrelse. For eksempel kan et 10 mm sigtehul producere partikler primært i området 8-10 mm.
Type af plastmateriale, der behandles:
- Hård, sprød plast (f.eks. PS, SAN, akryl): Disse materialer går let i stykker. Du kan muligvis bruge en sigtestørrelse, der er tættere på din ønskede partikelstørrelse. De kan dog også være slibende.
- Bløde, fleksible plasttyper (f.eks. LDPE, PP-film, TPE'er): Disse materialer kan være udfordrende. De har en tendens til at strække sig og deformere i stedet for at splintres. Mindre sigtehuller kan være nødvendige for at sikre effektiv skæring, men dette kan reducere gennemløbsmængden og øge varmeophobningen. Specialiserede "filmgranulatorer" har ofte specifikke sigtedesigns.
- Robust, slagfast plast (f.eks. PC, ABS, nylon): Disse kræver mere energi at granulere. Valg af sigte skal afbalancere partikelstørrelsen med granulatorens evne til at bearbejde materialet effektivt uden overdreven varme eller finpartikler.
Størrelse og form af inputmateriale:
- Store dele (f.eks. udrensninger, store støbte dele): Større, mere åbne sigter kan i første omgang overvejes for at give materialet mulighed for at blive "bidt" af knivene, men den endelige partikelstørrelse er stadig afgørende. Forhakning kan være nødvendig for meget store dele.
- Løbere og spruer: Disse er generelt nemmere at bearbejde.
- Film og ark: Kan vikle sig rundt om rotoren, hvis den ikke håndteres korrekt. Soldstørrelse og knivkonfiguration er afgørende.
- Nødvendig gennemstrømning (kg/time eller lbs/time):
Generelt giver større sigtehuller mulighed for højere gennemløb, da materialet forlader skærekammeret hurtigere.
Mindre sigtehuller betyder, at materialet forbliver i kammeret længere, hvilket reducerer gennemløbsmængden og potentielt øger finpartikler og varme. Du skal afbalancere den ønskede partikelstørrelse med dine produktionskrav.
Granulatorrotordesign og knivkonfiguration:
- Åben rotor: Bedre til varmefølsomme materialer og store dele, hvilket giver mere luftstrøm.
- Lukket (fast) rotor: Giver mere skærekraft til mere robuste materialer.
- Antal rotor- og underknive: Flere knive betyder generelt flere snit pr. omdrejning, hvilket kan give mulighed for lidt større sigtehuller, samtidig med at der opnås en mindre partikelstørrelse.
- Knivgab: Et korrekt indstillet knivgab er afgørende for effektiv skæring og fungerer sammen med skærmen.
Acceptabelt bødeniveau:
"Fint stof" er meget små partikler eller støv. For meget fint stof kan forårsage problemer i efterfølgende processer.
Mindre sigtehuller, især med bløde eller varmefølsomme materialer, kan nogle gange føre til øget mængde finpartikelspåner på grund af overslibning og varmeophobning.
Forståelse af skærmhullers former og mønstre
Selvom runde huller er de mest almindelige, findes der andre muligheder:
- Runde huller: Giver god partikelform og er branchestandarden til de fleste anvendelser. Giver god styrke.
- Firkantede huller: Mindre almindelig, kan nogle gange tilbyde en lidt højere gennemløbshastighed for et givet åbent område, men kan resultere i mindre ensartede partikler eller flere "haler" på partiklerne.
- Forskudte vs. lige mønstre: Forskudte mønstre (hvor huller i tilstødende rækker er forskudte) giver generelt bedre sigtestyrke og mere ensartet slid sammenlignet med lige rækkemønstre.
De procentdel af åbent område (det samlede areal af hullerne i forhold til det samlede sigteareal) er også en kritisk faktor. Et større åbent areal betyder generelt højere gennemløb, men det kan også reducere sigtestyrken.
Skærmstørrelsens indvirkning: En hurtig sammenligning
For at illustrere dette, lad os se på de generelle tendenser:
| Feature | Mindre skærmhuller (f.eks. 6-8 mm) | Større skærmhuller (f.eks. 10-15 mm+) |
|---|---|---|
| Partikelstørrelse | Mindre, mere ensartet | Større, potentielt mindre ensartet |
| Gennemløb | Sænke | Højere |
| Bødegenerering | Potentielt højere (hvis overslibning) | Generelt lavere |
| Energiforbrug | Potentielt højere output pr. enhed | Generelt lavere output pr. enhed |
| Varmeopbygning | Højere | Sænke |
| Egnethed | Applikationer, der kræver finslibning | Reduktion af mængder, færre kritiske specifikationer |
Bemærk: Dette er en generalisering. De faktiske resultater afhænger af materiale, granulatorens design og andre faktorer.
Praktiske tips til valg og optimering af din skærm
- Kontakt din granulatorproducent: De er din bedste første ressource. Giv dem oplysninger om dit materiale, inputformular og ønsket output.
- Start med en standardanbefaling: Hvis du er usikker, så start med en almindeligt anvendt størrelse til din materialetype (f.eks. 8 mm eller 10 mm for mange stive plasttyper).
- Test, test, test! Den bedste måde at finde den optimale skærm på er gennem empirisk testning. Kør forsøg med forskellige skærmstørrelser og analyser:
- Størrelsesfordeling af ommalet partikel (sigteanalyse)
- Gennemløbshastighed
- Tilstedeværelsen af bøder
- Temperatur på genformalings- og granulatorhuset
- Motorens strømforbrug
- Overvej en række skærme: Det er ofte en fordel at have et par forskellige sigtestørrelser ved hånden, især hvis du bearbejder forskellige materialer eller har skiftende specifikationer for slibning.
- Undgå at gå for småt unødvendigt: Brug af en meget mindre skærm end nødvendigt reducerer gennemløbshastigheden betydeligt og øger slid og energiforbrug.
- Undgå at gå for stort: Dette vil resultere i for store partikler, der kan være ubrugelige eller forårsage problemer nedstrøms.
- Inspicer og vedligehold skærme regelmæssigt: Slidte, beskadigede eller tilstoppede skærme reducerer ydeevnen drastisk. Udskift dem, når det er nødvendigt.
- Sørg for, at skærmene er installeret korrekt og sikkert.
Konklusion: Den rigtige skærm er nøglen til succes med granulering
At vælge den korrekte størrelse på din plastgranulatorsigte er et afgørende skridt i at optimere din plastforarbejdning og genbrug. Ved nøje at overveje materialetypen, den ønskede partikelstørrelse, gennemløbsbehovet og din granulators kapacitet, kan du vælge en sigte, der leverer genopmalet materiale af høj kvalitet, maksimerer effektiviteten og minimerer driftsomkostningerne.
Undervurder ikke kraften i denne enkle komponent. En velvalgt sigte kombineret med korrekt granulatorvedligeholdelse vil betale sig i det lange løb. Hvis du er i tvivl, bør du altid kontakte din udstyrsleverandør eller en granuleringsekspert. Du kan også udforske vores udvalg af plastgranulatorer for at se tilgængelige muligheder og sikre, at du træffer det bedste valg til dine specifikke behov.