How to Select the Right Plastic Granulator Blades to Improve Efficiency and Reduce Costs
Auswahl der geeigneten Kunststoff-Granulatorblätter is crucial for optimizing recycling operations, enhancing throughput, and minimizing maintenance expenses. Whether you’re an industrial equipment purchaser, engineer, or technical personnel, understanding the nuances of blade selection can lead to significant improvements in both performance and cost-effectiveness.
🧠 Understanding Plastic Granulator Blades
Plastic granulator blades are integral components in size-reduction machinery, designed to cut plastic materials into uniform granules for recycling or reuse. The choice of blade affects the granulation process’s efficiency, energy consumption, and the quality of the output material.
🔍 Key Factors in Blade Selection
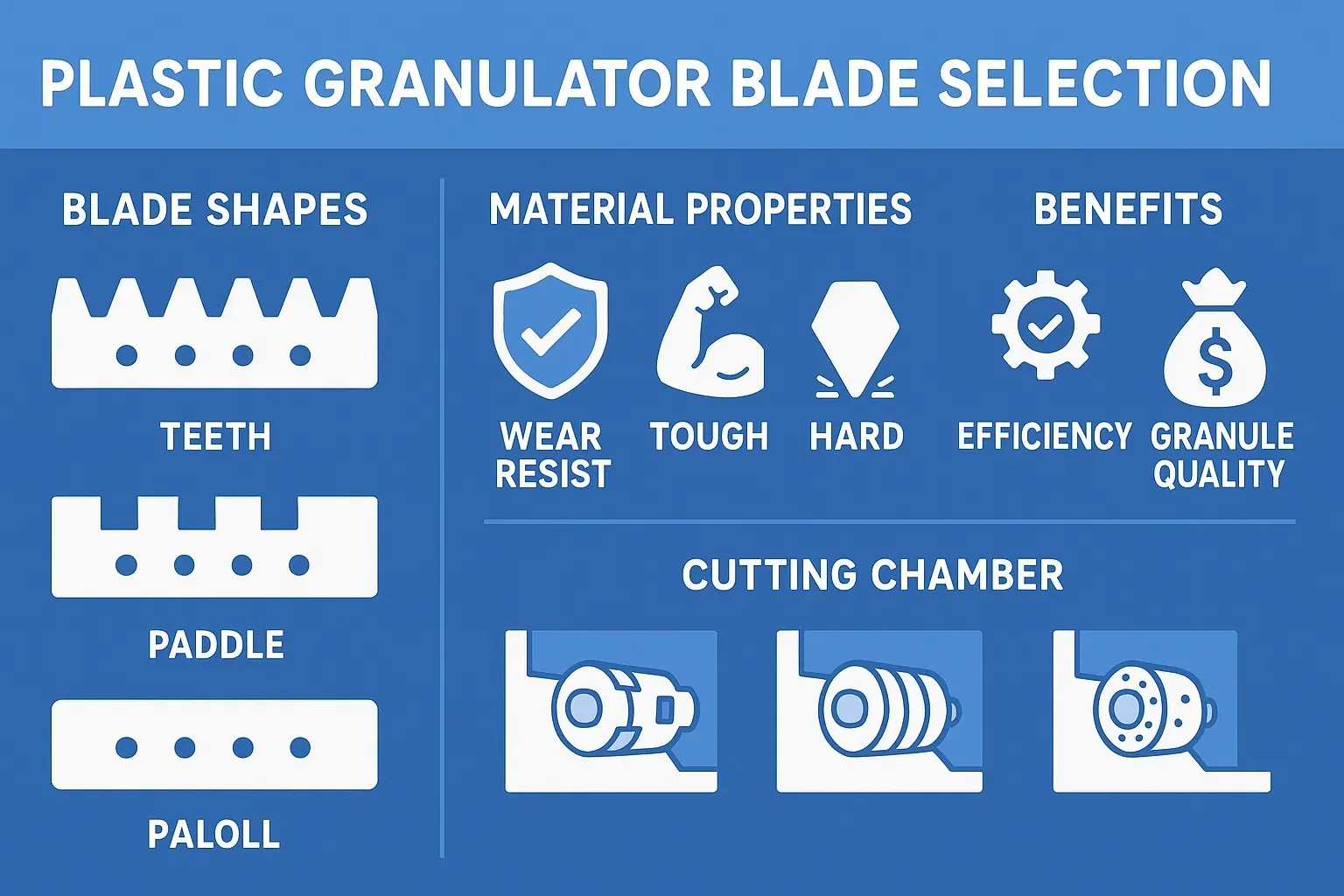
- 1. Blade Material
The material composition of granulator blades determines their durability, wear resistance, and suitability for specific applications. Common materials include:- SKD11: A high-carbon, high-chromium steel known for its hardness and wear resistance, ideal for general-purpose granulation.
- V-4E: A Swedish steel offering higher toughness and wear resistance, suitable for processing glass fiber-reinforced plastics.
- Wolframkarbid: Extremely hard and wear-resistant, used for abrasive materials or applications requiring extended blade life.
- 2. Blade Design
The configuration of blades influences cutting efficiency and material handling:- Teeth Blades: Feature serrated edges resembling a pineapple, effective for coarse grinding and reducing large plastic parts into smaller pieces.
- Staggered Blades: Arranged in a stepped pattern, these blades provide multiple cutting points, enhancing granulation efficiency.
- Paddle Blades: Designed with a scissor-like action, suitable for processing large or thick plastic items, offering gradual and efficient granulation.
- 3. Cutting Chamber Configuration
The design of the cutting chamber affects material flow and granulation effectiveness:- Tangential Chambers: Allow unrestricted airflow, ideal for heat-sensitive materials.
- Offset Chambers: Provide a direct path for materials, suitable for thick-walled plastics.
- Straight-Drop Chambers: Facilitate gravity-fed material entry, enhancing throughput for bulky items. (How to Choose the Right Granulator: A Three-Step Guide)
⚙️ Matching Blades to Applications
Selecting the right blade involves aligning material type, blade configuration, and chamber design with specific processing needs:
- Brittle Plastics: Use sharp blades with staggered or teeth configurations for efficient cutting. (5 Minutes to Understand Blades for Plastic Granulators)
- Thick-Walled Plastics: Opt for paddle blades and offset chambers to handle dense materials effectively.
- Heat-Sensitive Materials: Choose tangential chambers to minimize friction and heat generation.
💡 Tips for Cost Reduction and Efficiency
- Regular Blade Maintenance: Sharpening and timely replacement of blades prevent excessive wear and maintain cutting efficiency.
- Optimal Blade Material Selection: Investing in higher-quality materials may have a higher upfront cost but can lead to longer blade life and reduced replacement frequency.
- Proper Blade Alignment: Ensuring correct blade gap and alignment reduces energy consumption and improves granulation consistency.
🛠️ Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate plastic granulator blades is a multifaceted decision that impacts operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. By considering factors such as blade material, design, and chamber configuration, and aligning them with specific processing needs, industrial operations can achieve optimal granulation performance. Regular maintenance and thoughtful blade selection contribute to sustained efficiency and reduced operational costs.
For a more in-depth exploration of blade selection and maintenance techniques, refer to resources like Energycles guide on choosing the right plastic granulator blades.