Plastic pelletizing machines play a crucial role in converting plastic waste or raw materials into small granules, which are widely used in manufacturing injection-molded products, films, and sheets. Among the core processes of pelletizing, the cutting method directly influences the uniformity and quality of the granules. Based on existing research, the “cutting method” primarily consists of three techniques: gantry cutting, horizontal water ring cutting, and underwater cutting. These methods encompass both cold-cut and hot-cut techniques.
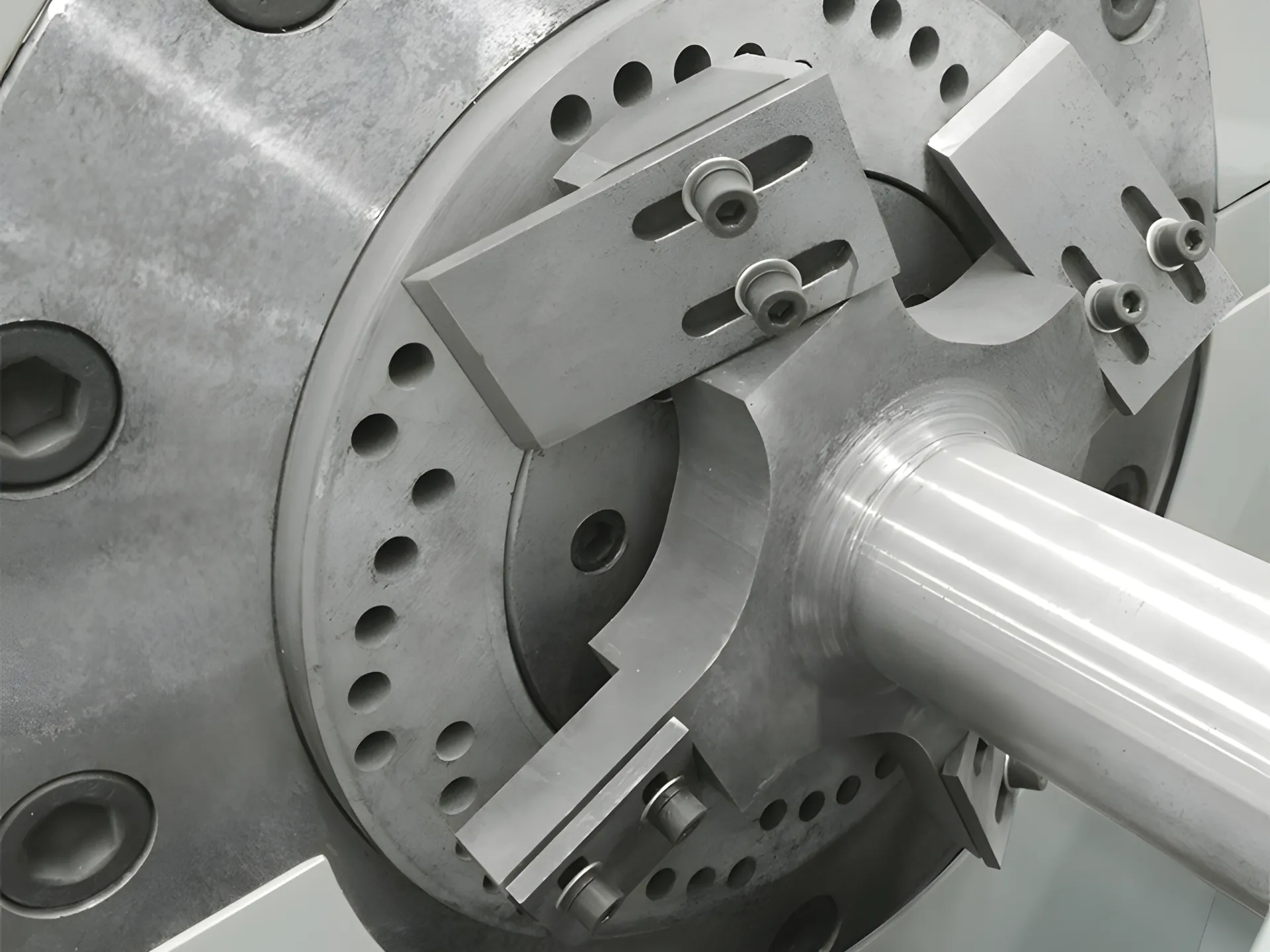
1. Gantry Cutting Machine
Gantry cutting is a cold-cutting method that falls under the category of strand pelletizing. The process operates as follows:
• The extruder forms plastic melt into long strands.
• These strands are cooled and solidified in a water bath to ensure shape stability during cutting.
• The cooled strands are fed into the gantry cutting machine, where the cutting blades, mounted on a gantry structure, ensure uniform pelletization by mechanically or pneumatically compressing the strands.
Advantages:


Applications:


2. Horizontal Water Ring Cutting
Horizontal water ring cutting is a hot-cutting method, classified as a variant of die-face pelletizing. The operational steps are as follows:
• The molten plastic is extruded through the die head in thin streams.
• A rotating blade set cuts the molten plastic at the die surface, forming initial granules.
• These granules are propelled into a horizontal water ring, where the circulating water cools them and removes excess heat.
This method is noted for its easy operation and maintenance, featuring a split design that facilitates cleaning and blade replacement. In the water ring system, molten polymer is extruded through a die and cut by concentric rotating blades, with the pellets carried into the water ring for cooling before being spirally conveyed to the drying stage.
Advantages:


Applications:


3. Underwater Cutting
Underwater cutting is another hot-cutting method, where the cutting process takes place entirely underwater. The workflow includes:
• Molten plastic is extruded through the die head directly into an underwater cutting chamber.
• Rotating blades cut the molten plastic in the water, where the granules are instantly cooled.
This method is particularly suitable for high-melt-index plastics and sinking materials, such as PP nonwoven and melt-blown fabrics. Underwater pelletizers (UWP) belong to the die-face cutting category and are ideal for handling high-output and specialty materials.
Advantages:


Applications:


4. Comparison and Selection Criteria
Choosing the right pelletizing method requires evaluating multiple factors. Below is a detailed comparison:
| Factor | Gantry Cutting Machine | Horizontal Water Ring Cutting | Underwater Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic Type | Engineering plastics (ABS, PA) | General-purpose plastics and some engineering plastics | High-melt-index plastics (PP nonwoven) |
| Pellet Quality | Smooth surface, uniform size | Even cooling, stable quality | Minimal oxidation, high quality |
| Production Efficiency | Suitable for small to medium batches, longer downtime | Continuous production, high efficiency | High throughput, ideal for special materials |
| Maintenance Cost | Complex maintenance, blade replacement requires downtime | Simple maintenance, fast blade replacement | Moderate maintenance, periodic water system checks required |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate water usage, requires drying | High water usage, but excellent cooling | High water usage, better for recycling applications |
When selecting a cutting method, manufacturers must assess material properties, production requirements, and cost considerations. One of the key debates is that underwater cutting, while suitable for high-melt-index plastics, may not be ideal for regions with limited water resources due to its high water consumption.
5. Conclusion
As a crucial component of plastic granulation, the cutting method encompasses gantry cutting, horizontal water ring cutting, and underwater cutting, each with its distinct applications. By understanding the advantages and limitations of each approach, manufacturers can optimize their production processes and achieve high-quality pellet output.
With the increasing emphasis on sustainability, underwater cutting and horizontal water ring cutting are expected to see greater adoption, especially in the recycling sector.