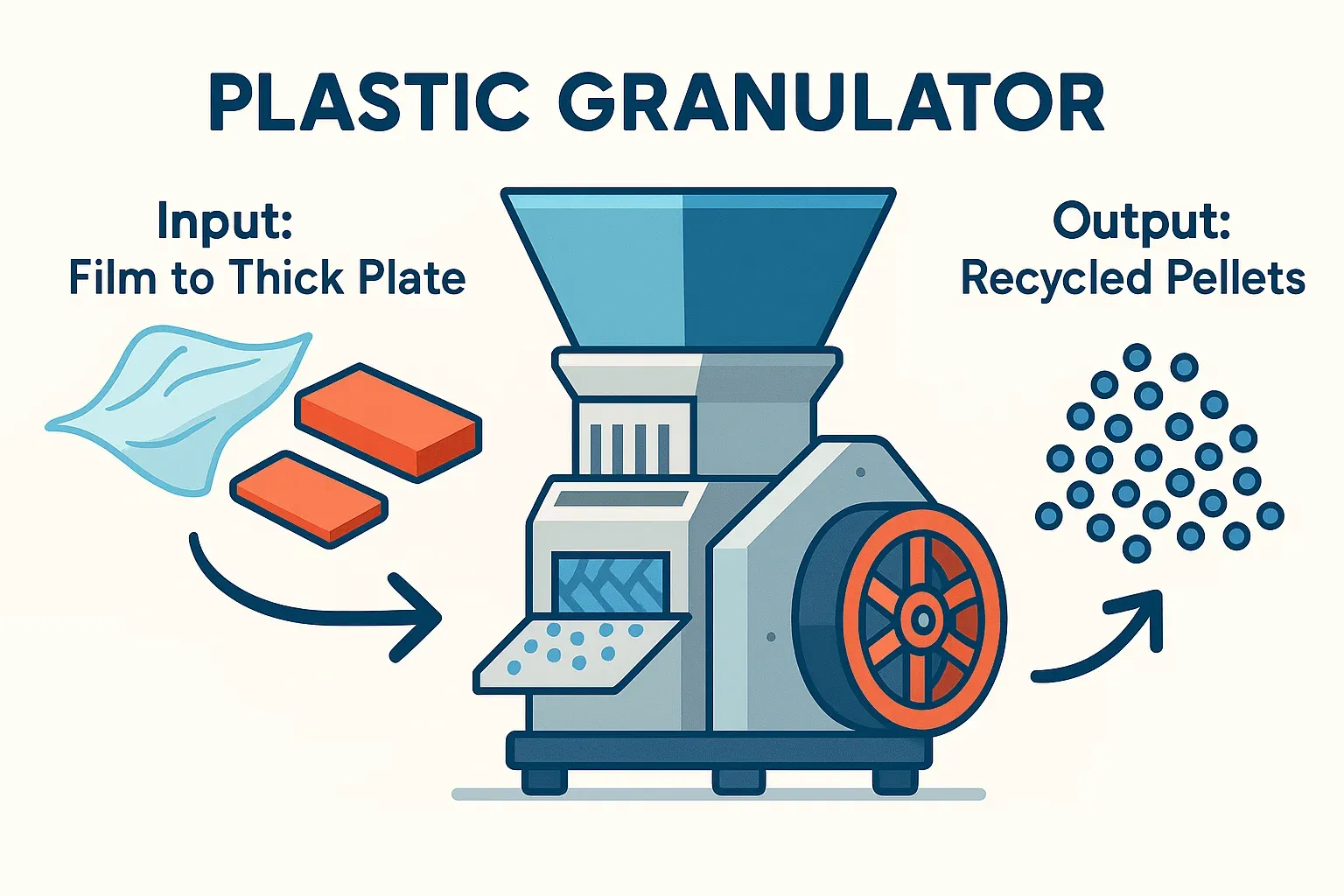
Versatile Size Reduction: Plastic Granulator Applications from Thin Films to Thick Plates
The global push towards sustainability and a circular economy has placed plastic recycling at the forefront of industrial innovation. As environmental concerns mount and regulations tighten, the demand for efficient recycling solutions is soaring. Market forecasts predict significant growth for plastic recycling equipment, with compound annual growth rates (CAGR) estimated between 4.5% and 6.4% globally through the early 2030s. Central to this growing industry is the granulador de plástico, a vital piece of machinery for processing diverse plastic waste streams.
For industrial equipment buyers, engineers, and technicians involved in plastics processing or recycling, understanding the capabilities and applications of granulators is crucial. These machines are not one-size-fits-all; their design and configuration determine their effectiveness in handling everything from flimsy packaging films to thick, rigid industrial plates. This article explores the wide-ranging application areas of plastic granulators, highlighting their versatility and providing insights into selecting the right equipment for your needs.
O que é um granulador de plástico?
At its core, a plastic granulator is a size-reduction machine. Its primary function is to break down large or bulky plastic items, scrap, or waste into smaller, consistently sized particles, often called “regrind” or “granules.” This process typically involves:
- Alimentação: Plastic waste is introduced into the granulator through a feed hopper.
- Corte: Inside the cutting chamber, rotating knives work against stationary bed knives to shear, cut, and fracture the plastic material.
- Triagem: A screen with specific hole sizes is located beneath the cutting chamber. Only particles small enough to pass through the screen exit the machine.
- Saída: The resulting granules are collected, ready for the next stage of recycling (like washing, drying, or pelletizing) or direct reuse in manufacturing processes.
Wide-Ranging Applications: Handling Diverse Plastic Forms
Modern plastic granulators are engineered to handle a vast spectrum of plastic materials and forms. Their adaptability is key to efficient recycling operations. Let’s explore how they tackle different types of plastic waste:
Processing Thin Films and Flexible Plastics
- Examples: LDPE/LLDPE packaging films, agricultural films, PP woven bags, flexible PVC sheets.
- Desafios: These materials are lightweight, can easily wrap around rotors, may cause feeding issues due to low bulk density, and require a clean cut to avoid fines or melting.
- Granulator Solutions:
- Cutting Action: A high-shear, scissor-like cutting action achieved through precise knife angles and rotor design is preferred. Paddle blades or specially angled rotor knives are often effective.
- Rotor Design: Open rotors can sometimes help, but specialized designs preventing film wrapping are crucial. Staggered knife patterns can distribute the cutting load.
- Alimentação: Tangential feed cutting chambers assist in directing the material effectively into the knives. Roll-feed systems are specifically designed for continuous film granulation directly from rolls.
- Evacuation: Proper air evacuation systems can help convey the lightweight regrind away from the cutting chamber efficiently.
Granulating Rigid Plastics and Molded Parts
- Examples: PET bottles, HDPE containers, injection-molded parts (ABS, PP, PS), automotive components (bumpers, dashboards), PVC pipes, crates.
- Desafios: These items can be bulky, have varying wall thicknesses, and require sufficient force to break down effectively.
- Granulator Solutions:
- Câmara de corte: Tangential cutting chambers excel at processing bulky, hollow parts by allowing a larger “bite.”
- Rotor Design: Both open and closed (solid) rotors can be used, depending on the specific application and desired throughput. Robust rotor and knife mounting is essential.
- Potência do motor: Adequate horsepower is needed to handle the initial impact and continuous processing of rigid materials without stalling.
Tackling Thick Plates, Sheets, and Purgings
- Examples: Thick extruded sheets (PC, ABS, HIPS), profiles, plastic lumber, large injection molding purgings, runners, or chunks.
- Desafios: These materials are dense, hard, and require significant cutting force. They can easily stall underpowered or improperly designed granulators.
- Granulator Solutions:
- Construção: Heavy-duty frame, rotor, and cutting chamber construction are non-negotiable.
- Câmara de corte: Straight-drop designs are often recommended for very thick materials.15 They allow the rotor knives to take smaller, sequential “nibbles” rather than attempting a large bite that could cause stalling.
- Motor & Drive: High-torque motors, potentially coupled with lower rotor speeds (low-speed granulators), provide the necessary force to cut through dense sections. Inertia from heavier flywheels can also help.
- Design da faca: Robust, potentially thicker knives are required. Teeth blades or staggered blade configurations can help grip and break down tough materials effectively.
| Feature Category | Thin Film / Flexible | Rigid / Molded Parts | Thick Plate / Purgings |
| Typical Materials | LDPE, LLDPE, PP Film, Bags | PET, HDPE, PP, ABS, PVC | PC, HIPS Sheet, Purgings |
| Key Challenges | Wrapping, Feeding, Fines | Bulkiness, Varying Thickness | Hardness, Density, Stalling |
| Cutting Chamber | Tangential, Specialized Feed | Tangential, Open Hopper | Straight-Drop, Heavy-Duty |
| Rotor/Knife Design | Scissor-Cut, Anti-Wrap | Robust, Open or Closed Rotor | High-Impact, Teeth/Staggered |
| Motor Emphasis | Speed & Clean Cut | Adequate HP for Bulk | High Torque, Heavy-Duty |
| Special Features | Roll Feed, Air Evacuation | Easy Hopper Access | Low Speed Option, Flywheel |
Key Factors for Selecting the Right Plastic Granulator
Choosing the optimal granulator requires careful consideration of your specific operational needs. Here are key factors to evaluate:
- Material Characteristics: What specific type(s) of plastic will you process? Consider hardness, abrasiveness, form (film, rigid, bulky), and maximum size/thickness.
- Requisitos de rendimento: How much material do you need to process per hour (kg/hr or lbs/hr)? Size the machine accordingly to avoid bottlenecks.
- Desired Output Granule Size: What particle size is required for your downstream processes? This determines the screen size needed. Consider consistency requirements as well.
- Cutting Chamber & Knife Design: Match the chamber geometry (tangential, straight-drop) and knife configuration (rotor type, blade type, number of blades) to your primary material type.
- Feeding Method: Will it be manual feeding, conveyor belt, robot, or roll feed? Ensure the hopper design is suitable and safe.
- Operational Considerations: Evaluate noise levels (low-speed models are quieter), dust generation (consider dust collection systems), and energy efficiency.
- Safety & Maintenance: Look for essential safety features (interlocks, rotor lock), ease of access for cleaning screens and changing knives, and overall durable construction.
- Orçamento: Balance the initial purchase price with long-term operating costs, including energy consumption, maintenance, and spare parts availability.
Conclusion: The Right Granulator Unlocks Recycling Potential
Plastic granulators are indispensable tools in the modern recycling and manufacturing landscape. Their ability to efficiently reduce the size of diverse plastic waste streams—from delicate thin films to robust thick plates—makes them critical for reclaiming material value and supporting the circular economy.
Selecting the right granulator, tailored to your specific materials and operational requirements, is key to maximizing efficiency, ensuring regrind quality, and achieving a strong return on investment. By understanding the different designs and their applications, you can make an informed decision that benefits both your bottom line and environmental goals.
We invite you to share your experiences! What types of plastic do you granulate? What challenges have you faced, and what solutions have worked best? Ask your questions or share your insights in the comments below – let’s learn from each other. If you need help selecting the right granulator for your application, don’t hesitate to reach out to our experts.