Recycling News
This article explains the seven main types of plastic, which materials are commonly recycled, what recycled plastics are used for, and the typical equipment required for each recycling process. A practical, engineering-focused guide for recyclers, plant operators, and project developers.
This article explains the main applications of PET flakes, common quality grades, and the technical indicators that determine their value—from fiber and sheets to bottle-to-bottle recycling. Ideal for recycling plant owners, equipment buyers, and project investors.
Rigid Plastic Recycling Trends 2026: The Industrial Buyer’s Guide to Profitable Sustainability
The landscape of rigid plastic recycling is shifting dramatically. As we approach 2026, the industry is moving beyond simple "waste reduction" into a highly regulated, profit-driven sector fueled by Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) laws and global circular economy mandates. For facility managers and recyclers, this is no longer just about being green—it is about operational survival and seizing market share.
Industry Insight: By 2026, the global recycled plastics market is projected to see aggressive growth, driven by new legislation in the US (like WA, CA, NJ) and the EU’s Circular Economy Act. The demand is shifting specifically toward High-Purity rHDPE and rPP that can rival virgin materials.
What Defines "Rigid Plastic" in an Industrial Context?
Before investing in machinery, it is critical to distinguish your material streams. Rigid plastics are dense, chemically resistant polymers that require heavy-duty processing. Unlike flexible films, they shatter or deform under high stress rather than stretch.
Common Industrial Rigid Streams:
- HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene): Detergent bottles, chemical drums, pipes.
- PP (Polypropylene): Car bumpers, battery cases, food containers.
- ABS/PS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene/Polystyrene): Electronic waste (WEEE) and appliance casings.
Processing these materials requires more than a standard shredder; it demands a calibrated system capable of handling high-impact loads and stubborn contaminants.
Key Trends Shaping Machinery Choices in 2026
1. The Rise of "High-Purity" Washing Lines
The market for low-grade regrind is shrinking. Buyers in 2026 demand 99.9% purity. This trend is driving a technological shift toward Hot Washing and Friction Washing technology.
At Energycle, we are seeing increased demand for integrated washing lines that can strip oils, chemical residues, and labels from rigid plastics (like HDPE milk jugs or PP oil containers) in a single pass. If your pellets smell or contain adhesive residue, they will sell for a fraction of the market price.
2. Automation and AI-Driven Sorting
With labor costs rising globally, the days of manual sorting lines are numbered. Modern recycling plants are integrating Optical Sorters (NIR technology) directly into their washing lines. These systems automatically eject non-target polymers (like a PVC pipe in a PP stream) before they hit the granulator, protecting your machinery and ensuring consistent output quality.
3. Closed-Loop Water & Energy Systems
Sustainability is not just for the plastic; it’s for the process too. 2026 regulations will scrutinize the water footprint of recycling plants. Leading machinery now incorporates:
30%
Less Water Usage via Filtration
VSD
Variable Speed Drives for Energy Savings
Machines equipped with water treatment recycling systems lower your operational overhead significantly over a 5-year period.
4. Handling "Difficult" Rigid Streams (EPR Compliance)
EPR laws are forcing manufacturers to take back difficult items like automotive battery cases and agricultural chemical drums. These are toxic and hard to process. Standard machines fail here. The trend is moving toward specialized Shredder-Granulator Combinations that can withstand heavy abuse and corrosive residues without frequent blade changes.
The Challenges You Will Face (And How to Solve Them)
✅ The Opportunity
- High Margins: High-quality rHDPE pellets are trading at premiums near virgin resin prices.
- Subsidies: Governments are offering grants for upgrading to efficient machinery.
- Scalability: Modular machinery allows you to start with 500kg/h and scale to 2000kg/h.
⚠️ The Obstacles
- Contamination: Paper labels, glue, and metal fragments can destroy extruder screws.
- Inconsistent Feedstock: Mixing different melt indexes causes pelletizing failure.
- Maintenance Costs: Cheap machinery vibrates excessively, leading to bearing failures and downtime.
Best Practices for Sustainable Operations
To ensure your facility remains competitive in 2026, adopt these operational standards:
- Invest in Pre-Shredding: Never feed whole bales directly into a granulator. Use a low-speed, high-torque shredder first to reduce wear.
- Filtration is King: Use dual-piston screen changers on your extruder. This allows you to swap dirty screens without stopping the machine, maintaining 24/7 production.
- Routine Blade Maintenance: Sharp blades produce less dust (fines) and use less energy. Establish a strict sharpening schedule.
💡 2026 Buyer’s Decision Guide
Before you purchase a Rigid Plastic Recycling Machine, ask the manufacturer these questions to ensure E-E-A-T compliance and ROI:
- Does the washing line include a hot washer? (Essential for removing glues and oils from rigid containers).
- What is the steel grade of the screw and barrel? (Look for bimetallic treatment to resist abrasion from dirty plastics).
- Is the water system closed-loop? (Crucial for lowering utility bills and meeting environmental permits).
- Do you offer local commissioning and spare parts? (Downtime kills profit; ensure your partner is accessible).
Why Energycle? The Advantage for Professional Buyers
The recycling industry is flooded with generic machinery that looks good on paper but fails under the stress of 24/7 industrial operation. At Energycle, we don't just sell machines; we engineer turnkey recycling solutions tailored to the 2026 regulatory landscape.
Our Rigid Plastic Washing & Pelletizing Lines are built with heavy-gauge steel and precision-engineered components designed to handle the toughest loads—from HDPE drums to PP crates. We prioritize Intelligent Automation, allowing you to monitor energy consumption and output quality in real-time.
Ready to Upgrade Your Recycling Infrastructure?
Don't let outdated machinery hold your business back. Embrace the 2026 trends with equipment built for efficiency and high-purity output.
Get a Custom Solution Quote
Europe is at the forefront of the global circular economy. With strict environmental regulations, ambitious recycling targets, and rising demand for high-quality recycled plastics, European recycling plants require reliable, compliant, and energy-efficient plastic recycling equipment.
This guide explains what European recyclers look for when investing in plastic recycling machinery—and how to select the right equipment for long-term success.
1. Why European Recycling Plants Have Higher Equipment Requirements
Unlike many other markets, European recycling facilities must operate under tight regulatory, safety, and quality constraints. Equipment decisions are influenced not only by price but also by:
- EU recycling policies and waste management directives
- CE safety and compliance requirements
- Energy efficiency and reduced carbon emissions
- Water consumption and wastewater recovery
- Output quality (especially for food-grade and closed-loop recycling)
As a result, plastic recycling equipment for Europe must be engineered differently, with a stronger focus on automation, process stability, and compliance.
2. Core Plastic Recycling Equipment Used in European Plants
A modern European recycling plant consists of several interconnected systems rather than standalone machines. These systems must work together to ensure consistent quality and high throughput.
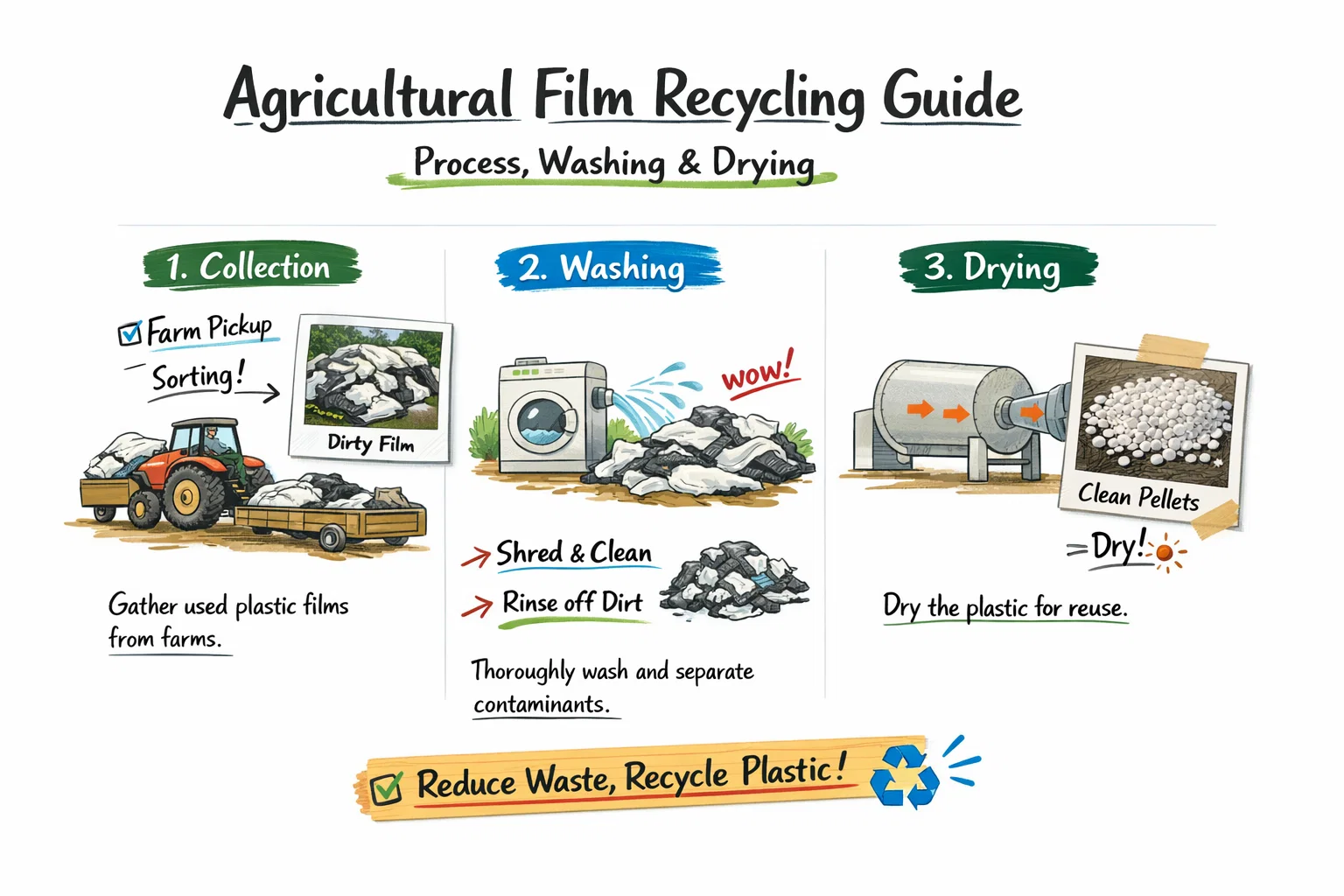
2.1 Shredding and Size Reduction
The first step in many recycling operations is shredding and size reduction. European recyclers often process contaminated post-consumer plastics, so equipment must be robust and flexible enough to handle:
- Bottles, jars, containers
- Films and agricultural plastics
- Mixed polymers and labels
- Occasional metal contamination
Low-speed shredders and heavy-duty granulators ensure controlled size reduction with minimal wear.
2.2 Washing Lines – The Heart of the Plant
Efficient washing is the backbone of any plastic recycling plant. European facilities rely on advanced systems like the Recycling Washing System to deliver clean, dry plastic flakes ready for reprocessing.
Key Washing Line Technologies:
- Pre-washing and drum washing
- Hot washing systems (especially for PET)
- Friction washers
- Sink-float separation tanks
- High-speed centrifugal dryers
Efficient washing lines not only improve output quality but also reduce operating costs by saving water and energy.
2.3 PET Bottle Recycling Systems
PET is one of the most recycled materials in Europe, especially in countries with bottle deposit return schemes. For facilities processing PET, the PET Bottle Recycling System ensures top-tier cleanliness and consistent throughput.
These systems are engineered for:
- High-efficiency hot wash
- Label and adhesive removal
- Effective contaminant separation
- Consistent flake quality ready for further processing
European PET recyclers targeting food-grade or bottle-to-bottle applications place particular emphasis on hot washing and moisture-controlled outputs.
2.4 Rigid Plastic Washing Lines
Beyond bottles and films, rigid plastics like crates, drums, and industrial containers require specialized systems. The Rigid Plastic Washing Line for PP, HDPE, PVC is designed to process these challenging materials with high throughput and thorough cleaning.
These lines typically include:
- Heavy-duty pre-wash
- High-torque friction washers
- Aggressive decontamination systems
- Efficient drying solutions
Rigid plastic washing lines are increasingly in demand in EU markets processing packaging, industrial waste, and consumer goods plastics.
2.5 Drying and Dewatering Systems
After washing, moisture must be removed efficiently to prepare the material for extrusion or pelletizing. European recyclers often require high-performance drying systems such as those outlined on the Drying Systems page.
Effective drying is crucial for:
- Reducing final moisture below 1–3%
- Preparing flakes for consistent extrusion
- Lowering energy costs in downstream processing
3. Compliance and Certification in Europe
3.1 CE Certification and Safety Standards
All plastic recycling equipment installed in Europe must be CE-compliant, covering:
- Mechanical safety and guarding
- Electrical and control system certification
- Emergency stop systems
- Operator safety and ergonomic design
European buyers commonly request full CE documentation before progressing in purchase discussions.
3.2 Food-Grade and Bottle-to-Bottle Requirements
For recyclers aiming at bottle-to-bottle or food-grade PET recycling, additional scrutiny is applied to washing and decontamination processes. Washing systems must deliver consistent cleanliness and moisture control to meet stringent downstream requirements.
4. Energy and Water Efficiency – A Key Buying Factor
European recycling facilities are under constant pressure to reduce operating costs and environmental impact.
When selecting plastic recycling equipment, buyers focus on:
- Power consumption per ton of output
- Water circulation, filtration, and recovery systems
- Heat recovery in hot washing stations
- Automation and real-time process control
Equipment with optimized energy and water usage not only reduces OPEX but also enhances a plant’s sustainability profile—an important factor for EU funding, certification, and ESG commitments.
5. Turnkey Plastic Recycling Solutions
Many European buyers opt for comprehensive project solutions rather than isolated machines. The Recycling Solutions page highlights complete plant solutions, from initial layout design to installation and after-sales support.
Turnkey solutions typically include:
- Engineering and process design
- Complete equipment integration
- Installation and on-site commissioning
- Operator training and technical support
Such holistic services help recyclers reduce risk, improve uptime, and accelerate ROI.
6. How to Choose the Right Supplier for European Markets
When evaluating suppliers of plastic recycling equipment, experienced European recyclers look for:
- Proven installations in Europe or similar markets
- CE-ready machinery and documentation
- Engineering-led solutions rather than generic machines
- Transparent technical information and process support
- Long-term spare parts availability and service
Selecting the right partner is as important as selecting the right equipment.
7. Final Thoughts
European recycling plants operate in one of the most demanding regulatory and operational environments in the world. Investing in compliant, efficient, and integrated plastic recycling equipment increases profit margins, enhances product quality, and supports long-term sustainability goals.
With advanced washing systems, high-efficiency drying solutions, and turnkey recycling plant options, equipment suppliers can help European recyclers thrive in a competitive, compliance-driven marketplace.