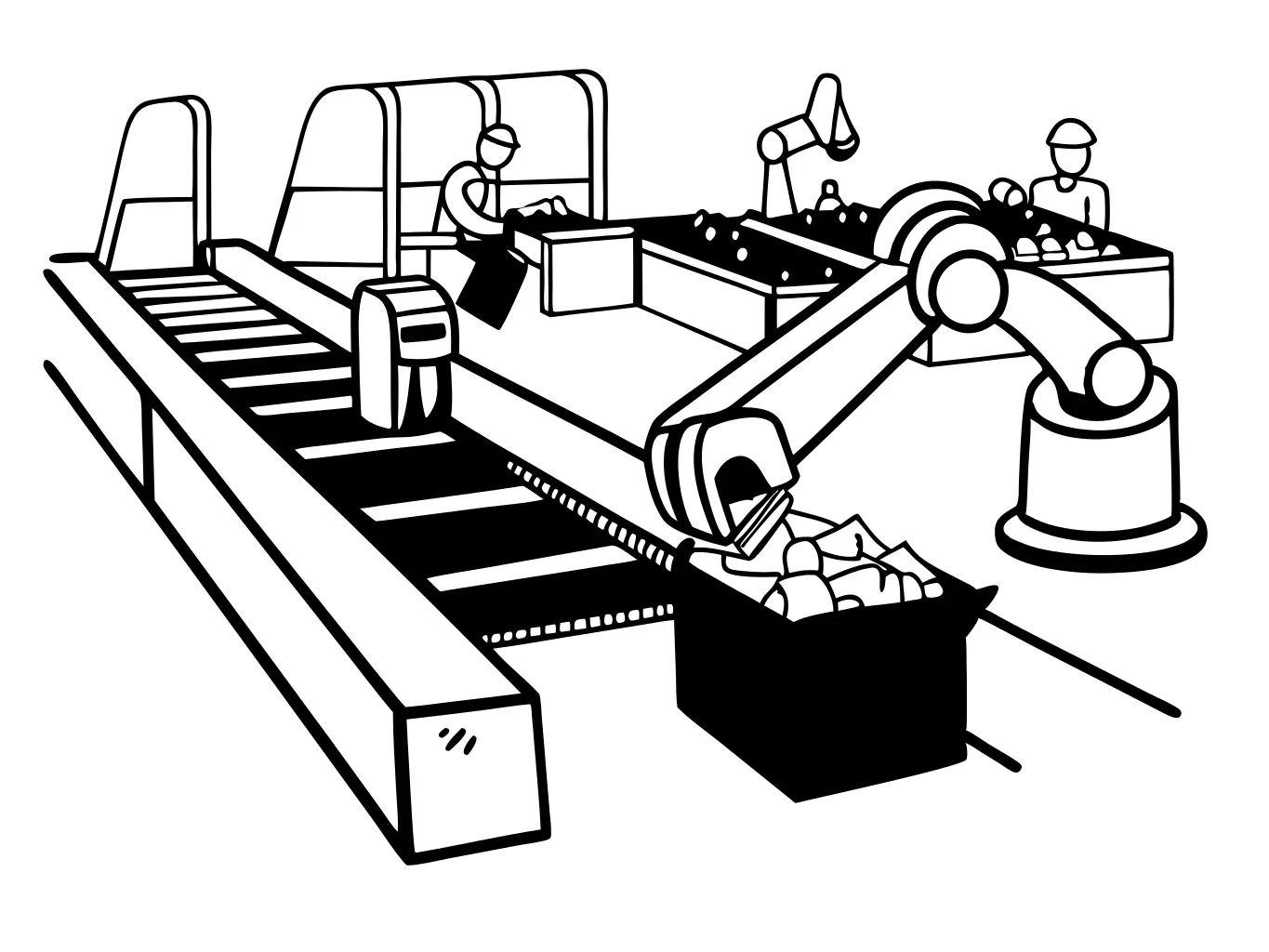
The global challenge of plastic waste has necessitated innovative solutions in recycling technology. One of the most groundbreaking advancements is the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into the sorting and processing of plastics. AI technologies are transforming the recycling industry by enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and the overall quality of recycled materials.
The Role of AI in Sorting Plastics
Sorting plastics has traditionally been a labor-intensive task, often prone to human error and inefficiency. However, with AI, companies like TOMRA have introduced systems like GAINnext, which leverage deep learning to identify and separate different types of plastics with unprecedented precision. This technology can distinguish between multi-layer packaging materials and even sort by transparency and color, which was previously challenging.
Advancements in Material Recognition
Recent developments have seen AI systems capable of identifying plastics based on hyperspectral imaging. This technology scans plastics’ chemical signatures, enabling a pixel-by-pixel analysis to categorize materials accurately. Not only does this increase the purity of the recycled output, but it also supports the processing of softer plastics like films and bags, which are notoriously difficult to recycle due to their tendency to tangle in machinery.
Robotics and AI at Work
The synergy between robotics and AI has led to systems like the Amp Cortex by AMP Robotics, which can sort up to 80 items per minute, recognizing over 50 billion objects to date across various facilities. These systems not only increase throughput but also adapt to the ever-changing nature of consumer waste, learning from each piece to improve sorting over time.
Economic and Environmental Impacts
The adoption of AI in recycling not only promises environmental benefits by reducing the amount of plastic waste in landfills but also has significant economic implications. High-quality sorting reduces contamination, thereby increasing the value of recycled plastics. This economic incentive can drive further investment in recycling technologies. The project OMNI, for instance, demonstrated how AI could be used to recycle food-grade polypropylene, opening up new markets for recycled materials in high-purity applications.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the advancements, there are challenges. The initial cost of AI and robotic systems can be high, though this is often offset by the reduction in labor costs and increased efficiency. Moreover, the rapid evolution of AI requires continuous updates to systems to keep pace with new types of plastics entering the market.
The Broader Perspective: Circular Economy
The integration of AI in plastic recycling is more than just technological progress; it’s a step towards a circular economy where materials are reused to their highest value. This aligns with global sustainability goals, as seen in initiatives like Unilever’s partnership with Alibaba to enhance recycling rates in China through AI-enabled machines.
Conclusion: The Road Ahead
As we move forward, the role of AI in plastic recycling will only grow. Innovations continue to emerge, with companies like Lauffer Vision Technology showcasing at the Plastics Recycling Show Europe how AI can further refine the recycling process. The journey towards a waste-free world where plastics are continuously cycled back into production is becoming more feasible with each technological stride.